Condroid
Android Container
Binder IPC Mechanism Multiplexing
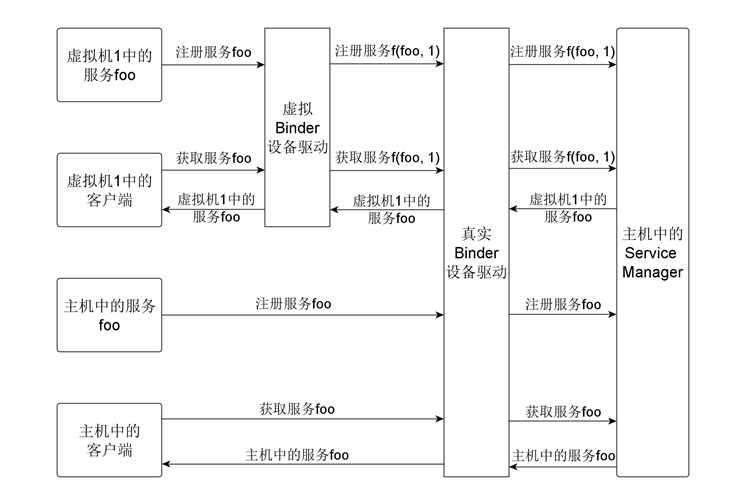
Binder IPC Mechanism Multiplexing,means that Host provide its core component(such as Binder device driver,Service Manager).Virtual machine has no these components,and its process use Binder IPC Mechanism through a virtual device indirectly.
To use Binder IPC Mechanism better,we choose virtual Binder device,not real Binder device.
Technical Proposal
1.Create Virtual Binder Device Driver
We add virtual Binder device driver in Android system,whose main functions is following:
(1)Call Binder device driver funtion,and transfer operations(open, ioctl, mmap) which applications do on virtual Binder device to real Binder device driver.
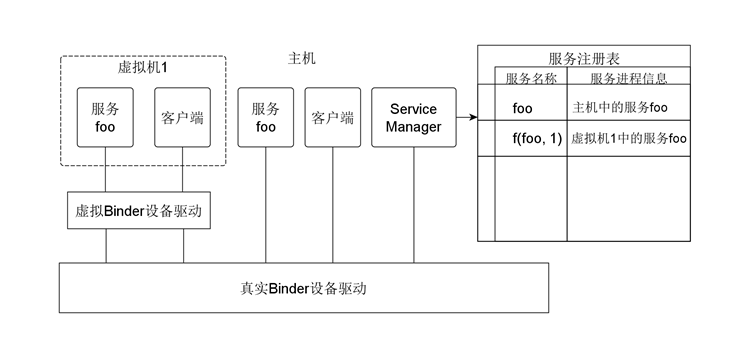
(2)Capture ioctl operation which applications do on virtual Binder device,filter registered service(launched by server process) and obtained service(launched by client process) which are sent to Service Manager,and use transfer function 'f' to modify service name in this 2 requests bdfore tranfering to real Binder device.
Tranfering device operation makes virtual Binder device has same function as real Binder device's.Modifying register service request makes same services running in different virtual machines register in Host's Service Manager with different names to solve problem of name conflict.Modifying obtain service request makes client process running in virtual machine get service in its same virtual machine,to solve problem of indistinguishable same services in different virtual machines.
2.Create and Allocate Virtual Binder Device
After creating driver procedure,we use it to register a group of Binder devices when initializing Linux kernel.It'll automatically create device file corresponding to these devices.Before booting the virtual machine,we bind Binder device file(/dev/binder) of root file system in virtual machine and a Host's virtual Binder device file together.Accessing /dev/binder in virtual machine means accessing Host's virtual binder device,so access operation will call functions in virtual binder device driver.
3.Sharing Service List
Since the limited resource of Android device,it'll reduce the operating performance of the single system to run serveral Android system on a device.In order to minimize Android virtualization performance penalties, we let some of the services that can be shared among multiple virtual machines run on the host, while the virtual machine does not start the services, and then by setting the list of shared services to implement shared services functions, thus reducing the total number of services that run on the device.
To this end, we create a file as a shared services interface in the proc file system, users simply write the service name of the file to set a specific service as shared service. Name of all shared services constitutes a list,which is stored in kernel memory space. Virtual Binder device drivers will firstly search for the service request list when modifying the registration service and getting the service.
If the service name is not in the list of shared services, modify it according to the established rules,else the Binder directly forwards the request to the real device driver. Virtual machine gets shared services will be obtained when the client process is running on the host services, these services are not running in the virtual machine.
Specific Technical Method
1.Create Virtual Binder Device Diver
Virtual Binder device driver is responsible for capturing, filtering and modifying process to the various operations of the Binder device, and then forwards the request to the real Binder device driver. The drive iswritten according to the Misc device driver model, code stored in conbinder.c.First you need to create a structure of type struct file_operations variable conbinder_fops, and function pointers in the structure corresponds to the various actions of virtual Binder device one by one. We need to write custom driver function of interception operations, used directly for operations that don't need to intercept the real function in the Binder device drivers. The implementations of the functions are shown in the following table:
| Operation on Device | Function Pointers | Implementation |
| open Binder device | .open | use binder_open function |
| query Binder device if it can read without blocking | .poll | use binder_poll function |
| send command to Binder device | .unlocked_ioctl | custom conbinder_ioctl function |
| used for 32-bit process in 64-bit system | .compact_ioctl | custom conbinder_ioctl function |
| map Binder's memory space to process's address space | .mmap | use binder_mmap function |
| execute buffered I/O operation | .flush | use binder_flush function |
| release Binder device | .release | use binder_release function |
2.Create and Allocate Virtual Binder Device
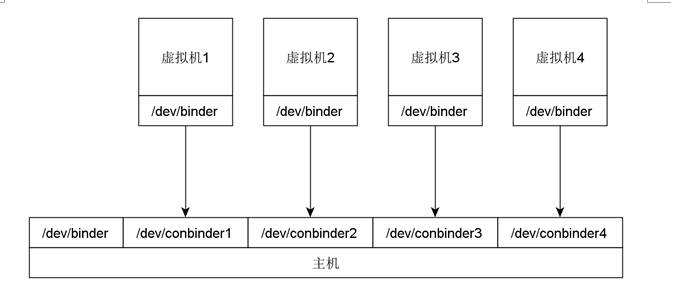
In order to make the kernel boot process creates a set of virtual Binder device, we write the conbinder_init function to initialize the virtual information of Binder device and register the device. First we define a group struct miscdevice type of structure body, thencall init_devs function to initialize these structure body in conbinder_init function, initial process include setting its minor (device ID), and name (device name) and FoPs (function pointer corresponding to each device), different structure body has different name field(contains each virtual Binder device ID), In other fields the same. FoPs field is set to the virtual address of the conbinder_fops structure in the Binder device drivers.
Conbinder_init function calls register_devs after the initialization, the latter loop calls the misc_register function to register a initialized virtual Binder devices in the kernel. So, the kernel will create virtual Binder device named after the device file in the/dev directory after startup. By using the bind option in mount command, you can bind these files and/dev/Binder files of the root file system in virtual machine , and assign them to the virtual machine. When applications access the Binder device in a virtual machine, the kernel will perform a virtual function in the Binder device drivers.
3.Interface of Sharing Service List
(1)Create file in proc file system:
The configuration interface of shared services list is implemented through the proc file system. We add code in the conbinder_init function, first call the proc_mkdir function to create a directory in the/proc directory, and then call the create_proc_entry in that directory to create a file named sharedservices, last create two functions conbinder_proc_ss_read and conbinder_proc_ss_ Write and set them to sharedservices file's read and write callback function.
(2)Define Data Struct of Sharing Service List:
After creating file , we allocate a block of memory in the kernel for the sharedservices file to write data, and then create a red-black tree-services_tree to index the file name stored in the shared services.
(3)Read and Write Sharing Service List:
When user writes the shared services name in sharedservices file, the kernel calls the conbinder_proc_ss_write function. The function stores the received data in the allocated memory block, and then inserts service names contained in data in services_tree. When user reads the sharedservices file, the kernel calls the conbinder_proc_ss_read function, the function reads the data in the memory block and returns to the top.
(4)Realize Sharing Service:
In order to achieve shared service functions, our virtual Binder device driver set a whitelist. If the service name of a intercepted request belongs to the white list, the request will not be modified. Thus, virtual machines do not need to run service client processes in whitelist.When client process in virtual machine requests a service from the whitelist to the Service Manager,service Manager returns service which runs on the host. Therefore,service in whitelist just runs on the host,shared by host and all client processes in the virtual machine. The whitelist is set to a red-black tree-services_tree. Virtual Binder device drivers will find the service name in a services_tree before modifying the request's service name , if not found then amending them; if found, discard your changes.
Reference Graph
The Overall Frame
Service Register Graph